Cataloger's Reference Shelf
MARC 21 Format for Bibliographic Data
Model A - Vernacular and Transliteration (Appendix D: Multiscript Records)
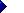 Example 1: Multiscript
record that follows Model A.
Example 1: Multiscript
record that follows Model A.
In this example, the language of cataloging is English language (Latin script) and the language of the bibliographic item is Russian (Cyrillic script). The cataloging agency provides transliteration of some Cyrillic script data into the Latin script; supplies notes, subjects, etc. in English; and prefers to use Latin script in the regular fields.

![]()
 Example 2: Multiscript
record that follows Model A.
Example 2: Multiscript
record that follows Model A.
In this example, the language of cataloging is English language (Latin script) and the language of the bibliographic item is Hebrew (Hebrew script). The cataloging agency prefers to use the Latin script in the regular fields.
The directionality of the Hebrew text in the example is right-to-left within each subfield, but the subfields themselves have been recorded left-to-right. The actual input of all the data is in logical order (first-to-last), parts of which may be displayed in various directions depending upon the script and the display interface.

![]()
 Example 3: Multiscript
record that follows Model A.
Example 3: Multiscript
record that follows Model A.
In this example, the language of cataloging and the bibliographic item is Arabic (Arabic script). The cataloging agency prefers to use Arabic in the regular fields.
The directionality of the Arabic text in the example is right-to-left within each subfield, but the subfields themselves have been recorded left-to-right. The actual input of all the data is in logical order (first-to-last), parts of which may be displayed in various directions depending upon the script and the display interface.

See also: